ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus.
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
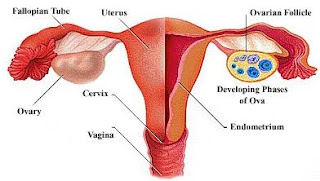
An ectopic pregnancy most often occurs in a fallopian tube, which carries eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. This type of ectopic pregnancy is called a tubal pregnancy. Sometimes, an ectopic pregnancy occurs in other areas of the body, such as the ovary, abdominal cavity or the lower part of the uterus (cervix), which connects to the vagina.
EARLY WARNING OF ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
Often, the first warning signs of an ectopic pregnancy are light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain.
If blood leaks from the fallopian tube, you may feel shoulder pain or an urge to have a bowel movement. Your specific symptoms depend on where the blood collects and which nerves are irritated.
EMERGENCY SYMPTOMS
If the fertilized egg continues to grow in the fallopian tube, it can cause the tube to rupture. Heavy bleeding inside the abdomen is likely. Symptoms of this life-threatening event include extreme lightheadedness, fainting and shock.
CAUSES
A tubal pregnancy — the most common type of ectopic pregnancy — happens when a fertilized egg gets stuck on its way to the uterus, often because the fallopian tube is damaged by inflammation or is misshapen. Hormonal imbalances or abnormal development of the fertilized egg also might play a role.
RISK FACTORS
Previous ectopic pregnancy. If you've had this type of pregnancy before, you're more likely to have another.
Inflammation or infection. Sexually transmitted infections, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia, can cause inflammation in the tubes and other nearby organs, and increase your risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
Fertility treatments. Some research suggests that women who have in vitro fertilization (IVF) or similar treatments are more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy. Infertility itself may also raise your risk.
Tubal surgery. Surgery to correct a closed or damaged fallopian tube can increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
Choice of birth control. The chance of getting pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) is rare. However, if you do get pregnant with an IUD in place, it's more likely to be ectopic. Tubal ligation, a permanent method of birth control commonly known as "having your tubes tied," also raises your risk, if you become pregnant after this procedure.
Smoking. Cigarette smoking just before you get pregnant can increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. The more you smoke, the greater the risk.
Complications
An ectopic pregnancy can cause your fallopian tube to burst open. Without treatment, the ruptured tube can lead to life-threatening bleeding
Prevention
There's no way to prevent an ectopic pregnancy, but here are some ways to decrease your risk:
Limiting the number of sexual partners and using a condom during sex helps to prevent sexually transmitted infections and reduce the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease.
Don't smoke. If you do, quit before you try to get pregnant
Drop your comments below and please do share!!!


Comments
Post a Comment